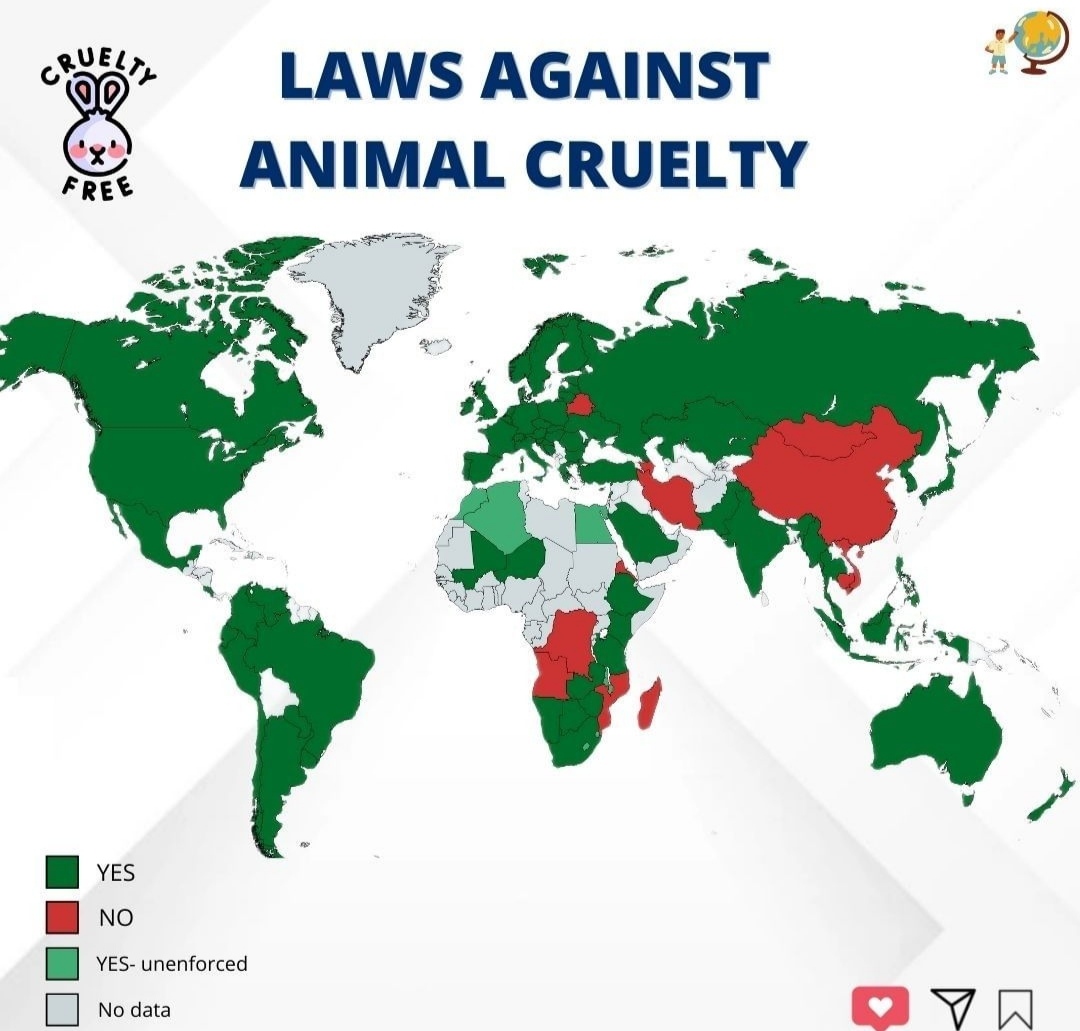
Animal cruelty is a pervasive issue that transcends borders, cultures, and societies. The treatment of animals has garnered increasing attention over the past few decades, and as a result, many nations have enacted laws aimed at protecting these vulnerable beings. However, the strength and scope of such laws vary significantly, revealing a complex tapestry of political, social, and moral attitudes towards animal welfare across the globe. This article seeks to provide a comprehensive overview of the countries that have instituted laws against animal cruelty, delving into the nuances of their legislation, enforcement, and broader implications.
In the United States, the landscape of animal cruelty laws is as varied as the nation itself. While animal protection laws exist at both federal and state levels, there is no comprehensive federal statute addressing all forms of animal cruelty. The Animal Welfare Act (AWA) governs the treatment of certain animals in research and agricultural contexts, but it falls short of covering many domestic pets and wildlife. State laws range dramatically, with some states enacting severe penalties for animal abuse, while others offer limited protection. The disparities often reflect cultural attitudes toward animal welfare and the influence of agricultural interests in certain regions.
In Europe, many countries have instituted robust animal protection laws. The European Union (EU) recognizes animals as sentient beings, which has led to a range of directives aimed at safeguarding their wellbeing. For instance, the EU has established regulations governing animal welfare in farming, research, and transport. Countries such as Germany and Austria have particularly stringent legislation. Germany’s Animal Protection Act, for example, affords comprehensive protections and mandates that animals be treated with respect and care—a reflection of the country’s deep cultural value placed on animal welfare.
Scandinavian nations are notable leaders in animal protection with their progressive laws and frameworks. Sweden’s Animal Welfare Act is celebrated for its stringent standards, including requirements for adequate living conditions and veterinary care. Norway follows suit with its own comprehensive legislation that promotes the welfare of domestic and wild animals alike. These countries leverage a strong public commitment to animal rights, a factor that is both sociologically and philosophically deep-seated in their populations.
Moving southward, Spain has made significant strides in recent years. The country is known for its rich cultural heritage intertwined with animal events, such as bullfighting, which has spurred discussions about ethical treatment. In 2021, the Spanish parliament approved measures to strengthen animal welfare laws, introducing harsher penalties for cruelty and restrictions on the use of animals in entertainment. This shift in policy not only reflects changing attitudes but also aims to align with broader European standards.
In contrast, countries in Asia present a mixed picture. Japan, for example, enacted the Animal Welfare Law, which provides some protections against cruelty, yet its enforcement can be lax. Cultural practices involving animals can complicate reform efforts, as traditional views may conflict with contemporary animal rights issues. Conversely, India has a more progressive approach with its Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, which has pioneered animal rights advocacy in the region. The country’s growing animal welfare movement is fueled by both governmental and non-governmental organizations working tirelessly to address injustices and advocate for stronger legislation.
Emerging economies also demonstrate varied commitments to animal protection. Brazil, for instance, has seen increasing awareness of animal rights, and many municipalities have enacted their own laws against cruelty. However, overarching federal legislation still requires reformation. Similarly, South Africa has implemented the Animal Protection Act, mandating humane treatment of animals and criminalizing acts of cruelty. The enforcement of these laws, however, often suffers from resource constraints and lack of public awareness.
In the Middle East, attitudes towards animal rights differ markedly. Some countries fall short in formal legal structures to prevent cruelty or protect animals. However, there is an emerging awareness of the importance of animal welfare due in part to global advocacy efforts, leading to improvements in certain regions. For example, the United Arab Emirates has recently taken steps toward strengthening animal welfare regulations, showing signs of a growing commitment to humane treatment.
Turning to Oceania, Australia has made substantial progress in animal welfare legislation. Each state and territory has enacted its own laws addressing animal cruelty, but the legal framework does lack uniformity. The Australian Animal Welfare Strategy aims to improve animal welfare standards across the board, influenced significantly by public sentiment and advocacy from various organizations. Despite these advancements, ongoing debates about practices like live animal export and animal use in entertainment underscore the complexity of achieving consensus on welfare standards.
Interestingly, the global landscape of animal welfare laws often mirrors broader themes of societal values and historical context. Areas with stronger animal rights movements tend to have cultural narratives that emphasize compassionate treatment and respect for non-human life. On the other hand, regions where exploitation is embedded in tradition confront significant obstacles in reforming legal structures. This ongoing discourse signifies a collective movement towards recognizing animal rights as integral to human ethics, revealing the interdependence of civilizations in their approach to compassion and respect for life.
In conclusion, the presence of animal cruelty laws worldwide is an evolving phenomenon that encapsulates various cultural, ethical, and political dimensions. As more nations begin to recognize the importance of protecting animals from cruelty, the journey toward comprehensive and enforceable animal welfare laws remains paramount. It is crucial for advocates and activists to continue pushing for reform, holding institutions accountable, and fostering a global perspective that elevates the rights of all sentient beings. This commitment not only reflects our collective moral responsibilities but also shapes the future of our interactions with the animal kingdom.