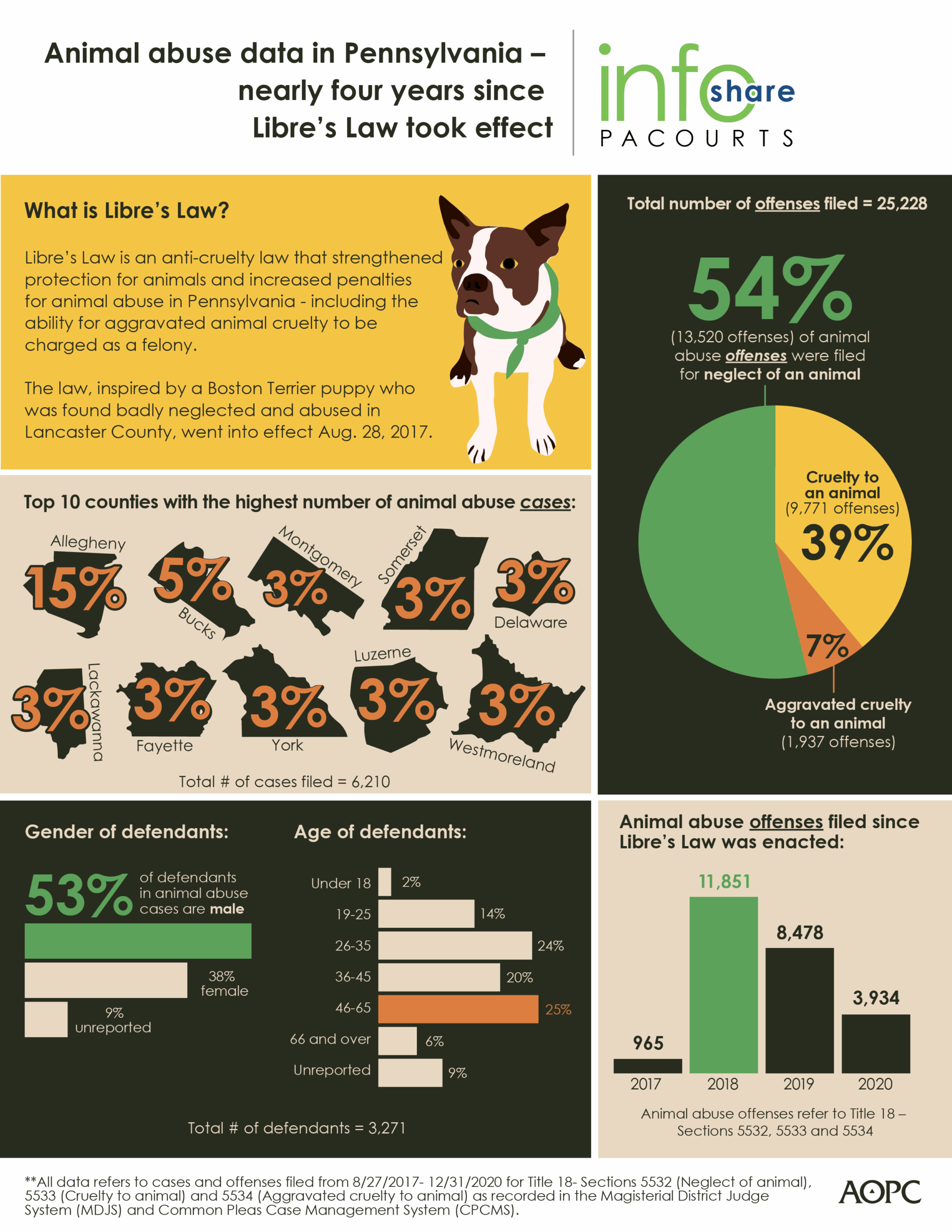
In recent years, the legal landscape surrounding animal cruelty has undergone significant transformations. Legislators across the world have begun to recognize and address the urgent need to protect animals from abuse and neglect. This article delves into the various laws that have been enacted, the implications they hold, and the evolving societal attitudes towards animal welfare.
Animal cruelty laws generally fall into two categories: criminal statutes and civil laws. Criminal statutes categorize certain acts of animal cruelty as offenses punishable by law, while civil laws often involve stipulations regarding the humane treatment of animals. The push for harsher penalties for animal abuse is driven not only by ethical concerns but also by mounting research linking animal cruelty to larger societal issues, including violence against humans. As such, legislators have increasingly sought to criminalize egregious acts of animal mistreatment.
One of the most significant movements in recent years has been the establishment of higher penalties for animal cruelty offenses. For instance, states like Florida and California have introduced legislation that imposes felony charges for severe acts of animal abuse. These laws often include provisions for mandatory psychological evaluations for offenders and may even impose lifetime bans on pet ownership. Such stringent measures underscore a growing acknowledgment of the societal implications of animal cruelty and the necessity of deterring such behavior through robust legal frameworks.
The implementation of laws specifically aimed at protecting animals in industrial farming has also gained momentum. For example, the passage of the Farm Animal Welfare Act in several states mandates that livestock must be provided with adequate space, water, and food. These regulations reflect a shift towards recognizing that even in agricultural contexts, humane treatment is paramount. Critics argue, however, that these laws need to extend further to include more stringent stipulations regarding the specific conditions that animals must endure in factory farming settings. Advocates for animal rights are pushing for bans on practices such as gestation crates and battery cages, recognizing these methods as forms of cruelty inherent to modern agricultural practices.
Another notable advancement in the realm of animal cruelty legislation can be seen in the movement to outlaw puppy mills. Puppy mill legislation, like that enacted in Illinois and Maryland, imposes strict regulations on breeders and mandates that they meet specific standards of care. This addresses a crucial issue where the breeding of animals is often conducted in deplorable conditions, leading to a multitude of health issues for the animals involved. These laws not only protect the animals but also promote ethical breeding, fostering a culture of accountability among animal breeders.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic shed light on the urgent need for legislative reform concerning animal cruelty, particularly in times of crisis. Animal shelters reported an increase in cases of neglect and abandonment, prompting lawmakers to consider temporary legislation aimed at protecting animals during emergencies. Laws enacted during this period included provisions for fostering animals from shelters to mitigate overcrowding and prevent neglect due to financial hardships faced by owners. Such adaptive measures reflect a growing recognition that animals should be included in discussions about public welfare during crises.
One area gaining traction is the importance of prohibiting the sale of animals in pet stores sourced from puppy mills. A growing number of municipalities have enacted ordinances banning the sale of pets from commercial breeders, encouraging adoptions from shelters instead. These laws promote awareness of the consequences of unethical breeding practices and aim to curb the perpetuation of animal suffering on a systemic level. By reducing demand for puppies sourced from mills, these ordinances foster a more humane approach to pet ownership.
The rise of technology has also dovetailed with efforts to combat animal cruelty. Animal Advocacy organizations have utilized surveillance and data analytics to capture evidence of abuse, pushing for stronger legislative responses. For instance, many jurisdictions have embraced the use of drones and cameras to monitor animal welfare in both domestic and agricultural settings. These technological innovations are invaluable tools for law enforcement, allowing them to investigate, document, and prosecute cases of animal cruelty more effectively than ever before.
Finally, the international community has begun to reflect on animal welfare with new lenses, evidenced by various treaties and agreements aimed at improving conditions for animals globally. For instance, the Animal Welfare Act of the European Union seeks to standardize animal protection measures across member states, emphasizing the need for cohesive policies that address animal welfare on a broader scale. This collective approach signifies a unified stance against cruelty and highlights the necessity for countries to work together in safeguarding the wellbeing of animals.
In conclusion, the past few years have witnessed a marked shift in the legislative context regarding animal cruelty. With a focus on harsher penalties, improved conditions for farm and shelter animals, and the use of technology in enforcement, progress continues to be made. These laws not only contribute to the protection of animals but reflect a broader societal commitment to addressing cruelty in all its forms. As the discourse surrounding animal welfare evolves, it is imperative for advocates, legislators, and the public alike to remain vigilant and proactive in the pursuit of humane treatment for all beings. Only through continued advocacy and legislative support can meaningful change be realized, ensuring that animals are treated with the dignity and respect they rightfully deserve.