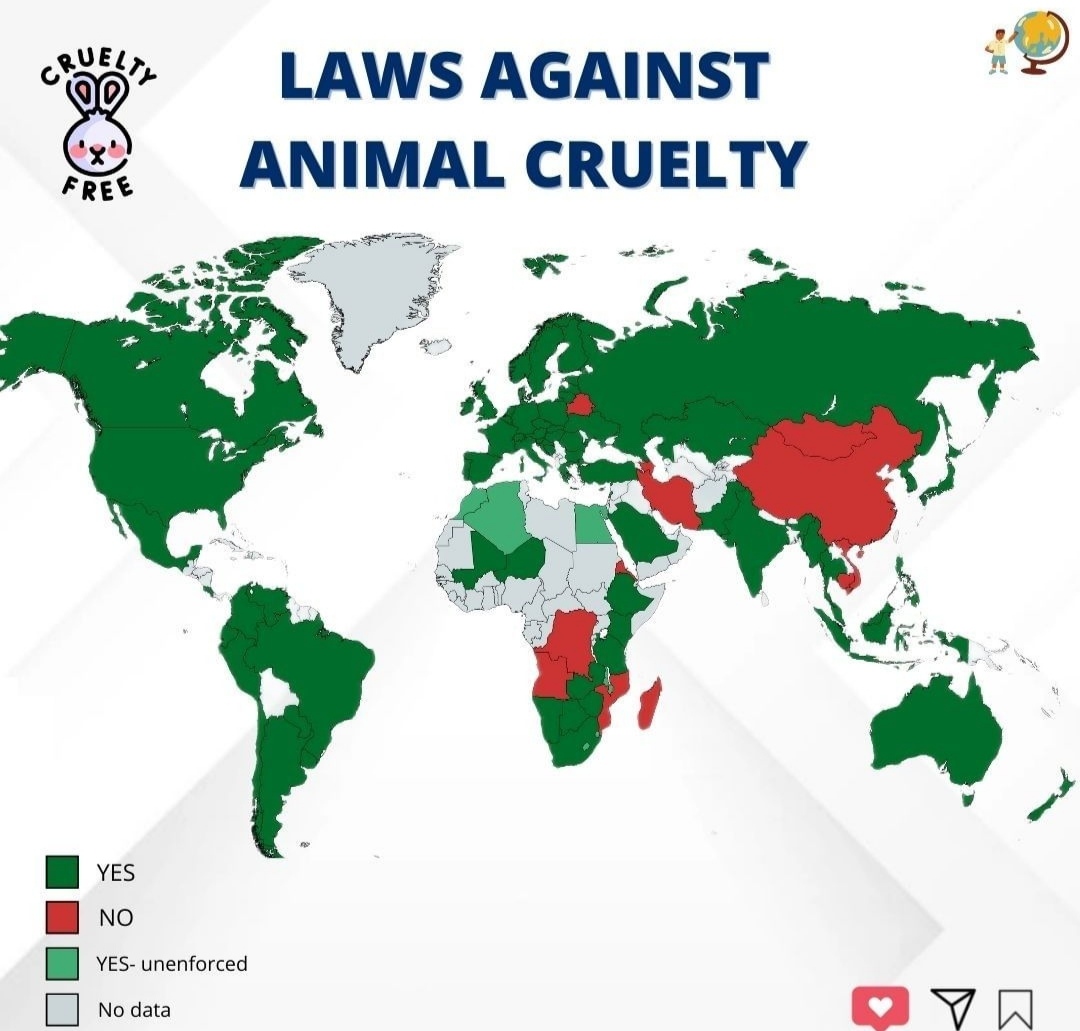
South Africa is renowned for its breathtaking landscapes and diverse wildlife, yet lurking beneath its stunning exterior lies a sobering issue: animal cruelty. The legal framework in South Africa regarding animal welfare is both vital and complex, serving as a deterrent against inhumane practices. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of the laws governing animal cruelty in South Africa, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of how these laws protect animals.
At the heart of animal welfare in South Africa is the Animal Protection Act of 1962. This legislation stands as a pivotal piece of the legal apparatus that shelters animals from cruelty and mistreatment. It sets forth a broad definition of what constitutes animal cruelty, encompassing actions that cause unnecessary suffering. This includes, but is not limited to, physical harm, emotional distress, neglect, and abandonment.
Further amplifying the legal efforts to protect animals, the Animal Welfare Act of 1997 introduced a more nuanced approach, delineating the responsibilities of pet owners and caretakers. This law emphasizes the ethical obligation humans have toward animals, mandating that every animal should have access to adequate shelter, food, and healthcare. The act also requires those who keep animals for commercial purposes to operate under humane conditions.
One of the notable facets of South African animal law is its categorization of cruelty. Violations can be classified into two primary segments: active cruelty and passive cruelty. Active cruelty involves willful acts inflicting pain, such as physical abuse or malicious torment. This can include anything from beating a dog to deliberately inflicting injury. Conversely, passive cruelty occurs through neglect, where animals suffer due to inadequate care or failing to meet basic needs.
The enforcement of these laws falls under the jurisdiction of various entities, including the South African Police Service (SAPS) and designated animal welfare organizations. The SPCA (Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals) plays a critical role in reporting and investigating instances of cruelty. They frequently collaborate with law enforcement to conduct inspections and enforce compliance with the law. Unfortunately, despite the legislative measures, enforcement remains inconsistent, often hampered by a lack of resources and public awareness.
Penalties for animal cruelty in South Africa vary significantly based on the severity of the violation. Minor offenses may lead to fines or community service, while more egregious acts can result in imprisonment. The legal consequences emphasize the seriousness with which society views animal abuse; however, there are ongoing calls for stricter penalties to deter potential offenders. Advocates argue that the current sentences do not adequately reflect the severity of the crime, particularly in cases involving extreme violence against animals.
Recent Developments in Animal Welfare Legislation
In recent years, there have been movements toward more robust animal welfare legislation in South Africa. These discussions are fueled by public outcry following high-profile cases of animal abuse that garnered media attention. Social media has also played a profound role, raising awareness and mobilizing community action against cruelty. This has led to renewed calls for reforms, aiming at updating existing laws to include contemporary issues such as factory farming, wildlife trafficking, and the treatment of animals in entertainment.
Understanding Your Role as a Citizen
As a member of society, understanding the laws related to animal welfare is crucial. Education plays a significant role in fostering a culture of compassion and respect for all living beings. Citizens are encouraged to inform themselves about local ordinances and to report instances of suspected cruelty to the appropriate authorities. Engaging with animal welfare organizations can also amplify community efforts in combating cruelty and promoting humane treatment.
Additionally, fostering a connection with local wildlife can enhance respect for these creatures and their habitats. Conservation efforts often go hand in hand with animal welfare; by safeguarding the environment, we protect the diverse species that inhabit South Africa. Educating the public about the importance of biodiversity and responsible wildlife tourism is essential for the long-term health of ecosystems and the animals that depend on them.
While the legal framework provides a foundation for protecting animals, the responsibility doesn’t solely rest with lawmakers and enforcers. Society must collectively advocate for change, encouraging a shift in public perception regarding animal rights and welfare. Volunteering, educating others, and supporting animal welfare organizations can considerably amplify these efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, animal cruelty is indeed illegal in South Africa, supported by laws aimed at curbing inhumane practices. While significant strides have been made toward a more compassionate society, the journey is far from over. Continuous advocacy, education, and vigilance are essential in ensuring that all animals are treated humanely. By fostering a culture that prioritizes animal welfare, South Africa can pave the way for a future where all living beings are respected and protected.