Animal welfare has transcended mere sentimentality and evolved into a paramount issue worldwide. Today, countries are recognizing the necessity of protecting animals from cruelty, but the extent and effectiveness of these protections vary significantly across the globe. Some nations stand out for their progressive laws and compassionate practices, while others lag behind, leaving millions of animals vulnerable. This article delves into the landscape of animal cruelty protections across various nations, exploring which countries lead in compassion and how effective their efforts truly are.
At the outset, it is crucial to define what constitutes animal cruelty. It encompasses acts that cause unnecessary pain, suffering, or distress to animals. This can manifest in numerous forms, including neglect, abandonment, physical abuse, and exploitation for entertainment purposes. Recognizing these practices, many countries have instituted laws aimed at curbing such behavior. However, despite the formation of protective regulations, implementation remains inconsistent, with loopholes still allowing for animal suffering.
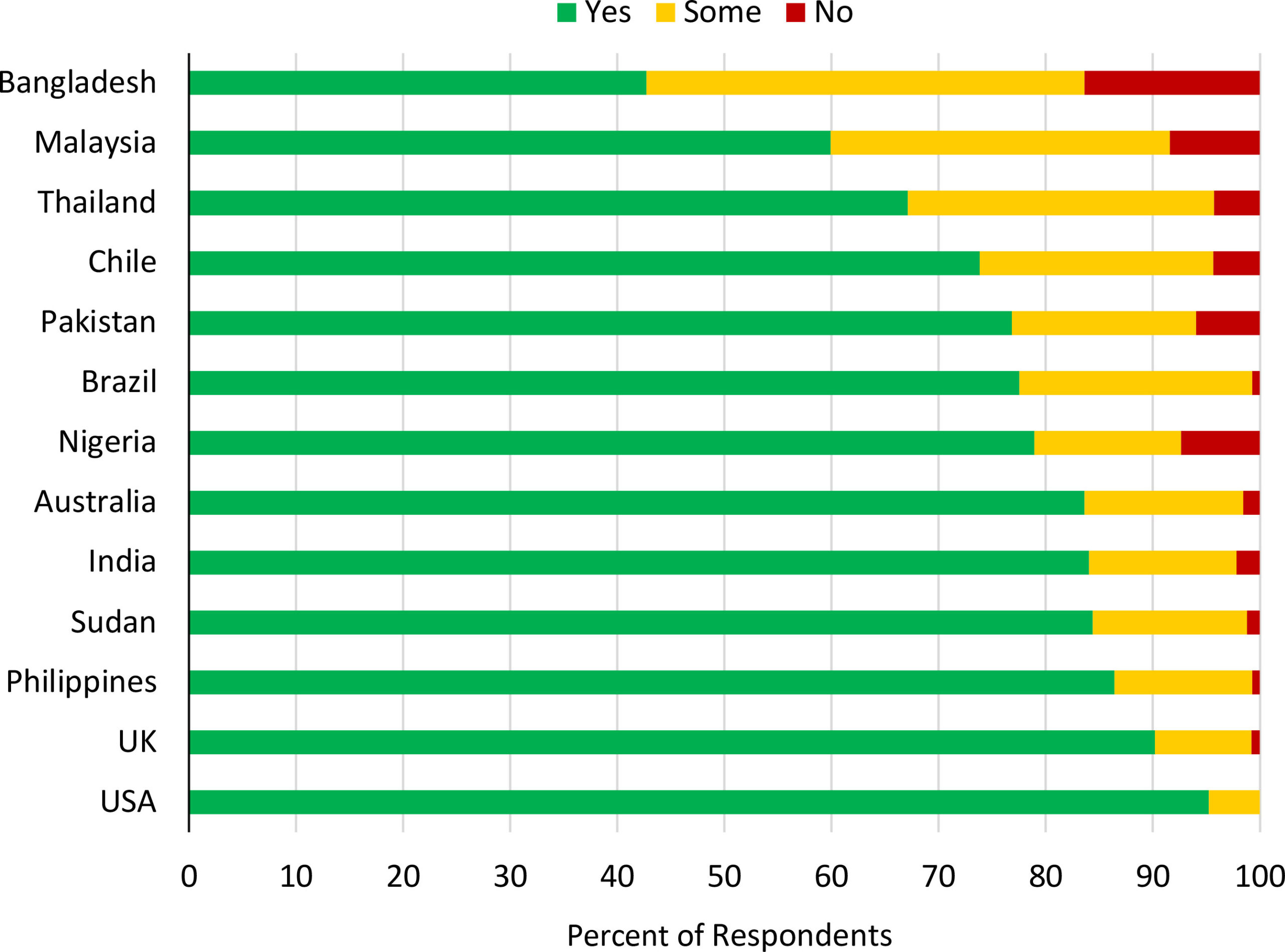
Astonishingly, the level of animal welfare legislation differs from one nation to another. As of recent evaluations, over fifty nations have enacted comprehensive animal cruelty laws. These laws vary in scope, often differentiating between pets, farm animals, and wildlife. In some cases, even the mere existence of legislation does not guarantee enforcement or compliance, leading to a spectrum of efficacy in actual protections.
Among the trailblazers of animal protection is Germany. Renowned for its robust animal welfare system, Germany’s constitution enshrines animal dignity as a fundamental aspect of societal values. This has led to the establishment of stringent regulations governing animal husbandry, transportation, and slaughter practices. The foundation of German animal protection law is not merely punitive; it fosters a culture of respect and care for animals, supported by comprehensive public education initiatives.
Close in line with Germany’s efforts are those of Switzerland, which boasts some of the strictest animal welfare laws globally. The Swiss animal protection framework includes laws that address the physical and psychological well-being of animals. For instance, animals are not merely considered property; they are recognized as beings deserving of appropriate living conditions, social interactions, and humane treatment throughout their lives. The Swiss populace overwhelmingly supports these measures, illustrating a national ethos that values animal well-being.
Turning to Scandinavia, countries like Sweden and Norway also assert their commitment to animal welfare through progressive legislation. Sweden’s Animal Welfare Act emphasizes the prevention of suffering and mandates that animals receive appropriate care. It includes strict animal husbandry requirements that promote the physical and mental well-being of domesticated animals. Similarly, Norway has implemented a comprehensive set of animal rights that covers both domestic and wild species, insisting on humane treatment balanced with conscientious use in agricultural and research contexts.
While some nations excel in animal protections, others face considerable challenges. In the United States, for example, the treatment of animals varies drastically depending on state laws. Federal legislation such as the Animal Welfare Act establishes minimal standards for the treatment of certain animals; however, it has significant limitations. The law does not extend to farm animals or many species utilized in research and entertainment. Consequently, an unfortunate number of animals endure neglect and maltreatment. Public opinion increasingly favors stronger protections; yet, legislative progress remains slow and uneven.
In Asia, countries like India have made strides with the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, which aims to protect animals from abuse. Nevertheless, enforcement is sporadic, and cultural attitudes toward animals can impede progress. Despite these hurdles, animal activism is gaining traction, catalyzed by a growing awareness of animal rights and welfare issues among the urban population.
Moreover, nations in the developing world frequently grapple with conflicting priorities. In many cases, socioeconomic challenges overshadow animal welfare concerns. While some countries aspire to establish legal frameworks to combat animal cruelty, they often lack the resources, infrastructure, and public support necessary for adequate enforcement. Thus, animals in these regions often remain at risk, subjected to cruelty and neglect without recourse or protection.
In contrast, countries like Brazil have seen an emergence of animal welfare laws in recent decades, motivated by internal movements that advocate for better treatment of animals. Brazil’s Federal Law on Animal Protection establishes penalties for abuse and outlines proper treatment standards for domestic animals. However, like many other nations, the implementation of these regulations is hindered by corruption and a lack of commitment among local authorities.
As we reflect on the global landscape of animal cruelty protections, it is evident that the response to animal welfare is as varied as the nations themselves. A tapestry of legal frameworks, cultural attitudes, and ethical considerations shapes the treatment of animals around the world. Where comprehensive municipal or national protections exist, they often stem from a deep-rooted societal belief in the importance of compassion and stewardship for animal life. Nations leading in compassion not only enforce laws against cruelty but also foster holistic approaches through education, advocacy, and community engagement.
The journey towards a more compassionate world for animals is ongoing. As awareness continues to grow, the hope remains that more countries will recognize the intrinsic value of animal life, enacting and enforcing protections that reflect a commitment to compassion and justice. The future depends on collective action from individuals, grassroots movements, and policymakers alike, working cohesively to end animal cruelty worldwide.